Install fraud
Proxy tunneling
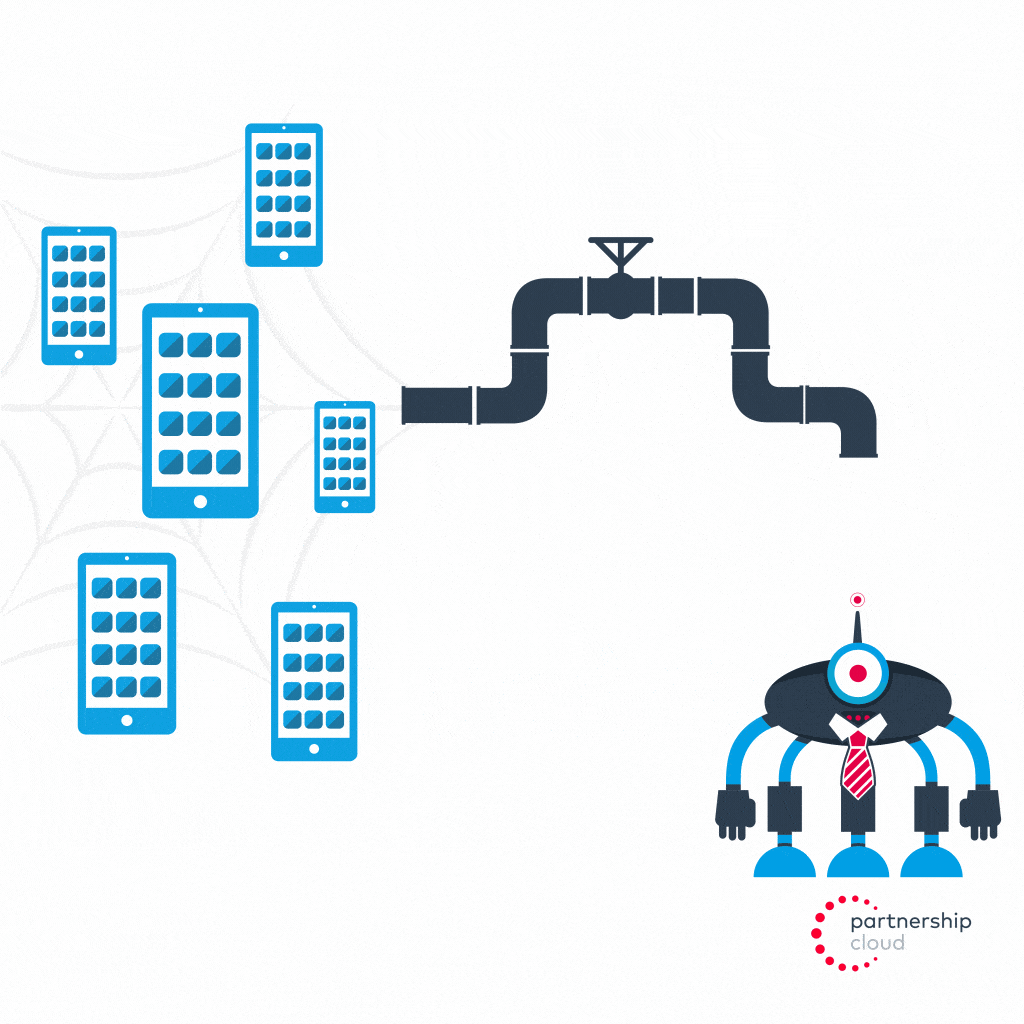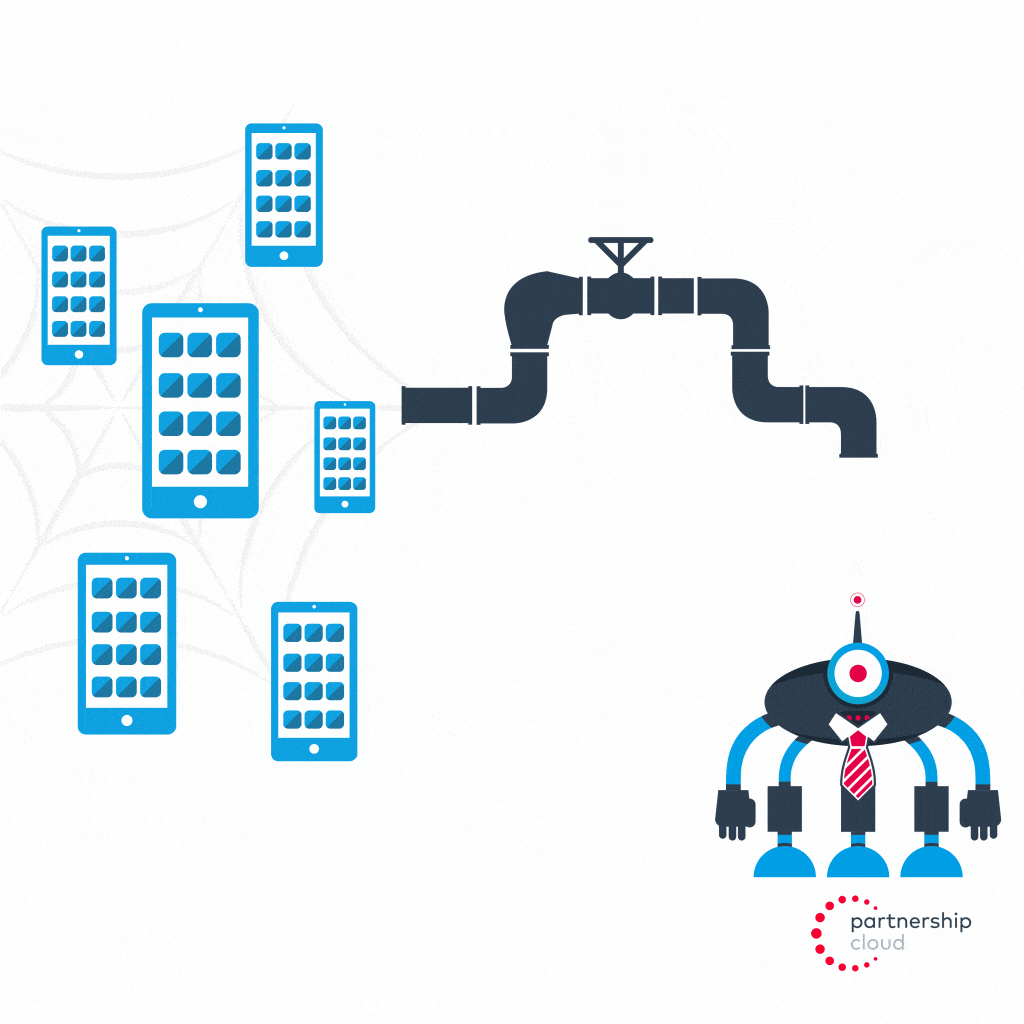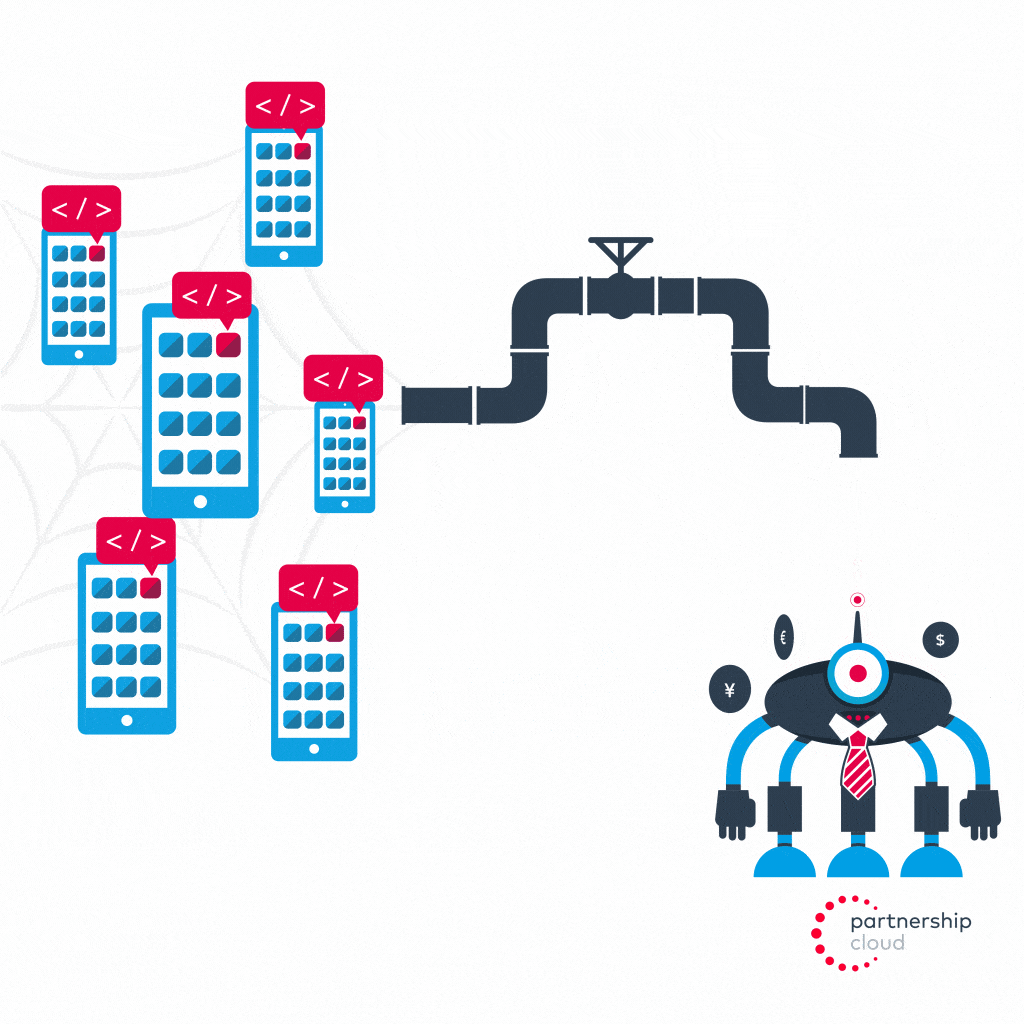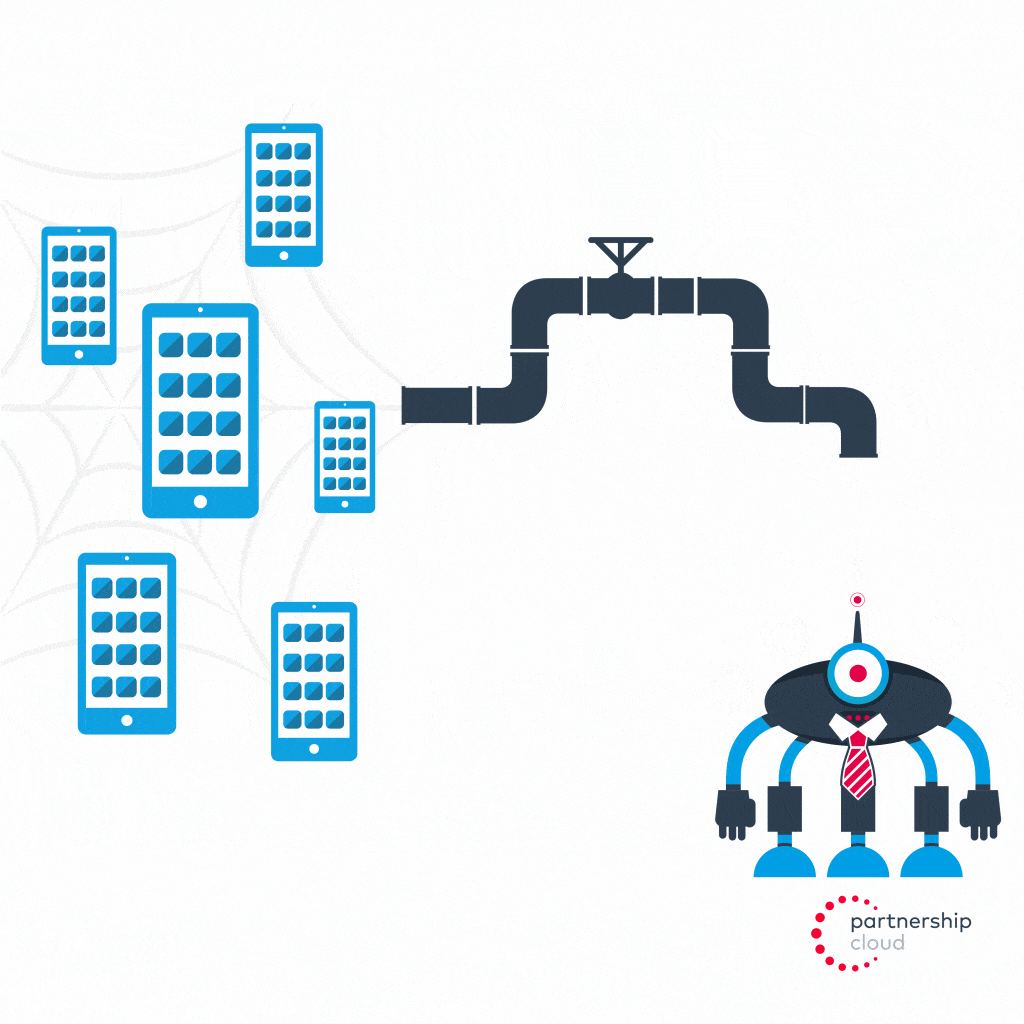
A malicious app, installed across a large share of mobile devices, can install malware that effectively converts that network of phones into a mobile botnet. This mobile botnet is remotely controlled by a botnet operator, which can leverage the hijacked IP of the device to mask the location of the operator while committing install fraud on a large scale.
How they do it
- Malicious publisher has registered for advertiser’s large CPI program
- User downloads malicious publisher’s app
- App installs malware that makes user’s device a member device of an operator’s botnet
- Botnet operator reverse engineers the postback codes sent by advertiser’s app from its tracking software development kit (SDK) to the SDK’s servers
- Botnet operator tunnels through proxy to instruct user’s infected device to send out a fake, manipulated postback signal to the same SDK servers to indicate that an install has taken place (even though it has not and user is none the wiser)
- Advertiser attributes credit to malicious publisher, even though they provided no value and did not actually drive an install, and pays them a percentage of revenue