What is affiliate marketing and how to get started?
Affiliate marketing is a $12 billion industry* globally, with $6.8 billion of that figure coming from the United States alone. Even during uncertain times, affiliate marketing remains a top-performance channel. And for marketers, affiliate marketing also recently ranked as a top in-demand skill*. That’s because of its high earnings potential for advertisers and affiliates alike.
For brands, affiliate marketing can deliver up to 30 percent or more of total revenue, with an impressive average return on investment (ROI) of $15 for every dollar spent. Meanwhile, affiliate publishers with lucrative partnerships can earn up to $10,000 a day*. Or, at the very least, they can diversify and level up their earnings through brand partnerships.
Whether you’re a new or aspiring advertiser or affiliate, this ultimate guide to affiliate marketing will set you on the right path. It’s a step-by-step guide that teaches you the basics on how to get the best out of the channel.
In this guide you’ll discover answers to questions like:
1. What is affiliate marketing?
Affiliate marketing is a performance-based marketing channel. Brands reward affiliate publishers for driving traffic or sales to their website.
Let’s start with a breakdown of the four major parties involved in affiliate marketing:
- Affiliates — Individuals or companies that get paid to generate clicks, leads, and/or sales for advertisers. Also called publishers or partners.
- Advertisers — Companies that pay commissions to affiliates that drive traffic to their website. Also called enterprises, merchants, or brands.
- Consumers — The end users or potential customers that click an affiliate’s link. Consumers visit an advertiser’s website and sign up or buy a product or service.
- Affiliate platforms — A technology solution that helps connect advertisers and affiliates. Generally provides tracking, contracting, reporting, and payment capabilities.
An affiliate usually owns a website or a social property. It promotes an advertiser’s brand through a trackable link.
An affiliate link is usually included within a:
- Blog post
- Coupon page
- Product review
- Banner advertisement
- Product comparison portal
- Email campaign
- Social media channel
How does affiliate marketing work?
The concept of affiliate marketing may be difficult to understand at first, so let’s break it down.
When an affiliate (partner or publisher) joins a brand’s affiliate program, the brand provides the affiliate with access to unique tracking links. The affiliate then promotes the brand using these links. The affiliate can add the links to its website, social profiles, email campaigns, and other promotional opportunities.
Consumers click on these links, which bring them directly to the brand’s website to make a purchase. The affiliate receives a commission from the brand for any purchase a consumer makes.

Example: Let’s say the affiliate is a vlogger (video blogger) who hosts a sneaker review series. A consumer clicks on the vlogger’s recommendation link to buy a pair of sneakers. The vlogger secures a sale for the sneaker brand and receives a commission in return.
How do affiliate commissions work?
Affiliate marketing operates on a performance-based model. Affiliates gain commission payments when specific “conversion events” take place. A conversion event could be any number of actions a user takes on-site, for example, a product sale, a newsletter sign-up, or an account registration.
The affiliate performance-based model generally uses a set of standard payment structures, including:
- Cost per action (CPA)
- Cost per lead (CPL)
- Cost per click (CPC)
How do affiliate payments work?
In the past, affiliates were only paid when they generated the last click to sale, i.e., the click that guaranteed the sale. Now, many enterprises customize payouts and decide which actions to compensate — and how. Commissions can now be set on alternative goals, such as:
- First click to site
- Conversion path participation
- Monthly performance thresholds
- Customer status
- Promo code
- Certain SKUs
This type of flexibility and diversification on payments is great news for affiliates.
Brands now understand the role affiliates play in the full consumer journey. As a result, affiliates can now be paid for playing a part in moving a customer toward a sale — whether through awareness, engagement, first click, or last click.
Why use affiliate marketing?
Affiliate marketing is popular because it’s reliable and affordable for all parties. And more and more brands are recognizing the uncapped potential of partnerships. Today, more than 15 percent of all digital media revenue* comes from affiliate partnerships. On average, high-maturity partnership programs contribute 28 percent of a brand’s overall revenue*.


Affiliate marketing is a flexible channel that helps brands reach new audiences, grow revenue, and efficiently scale. Brands only pay when results are achieved, which means the channel carries low risk and high growth potential. A great example of successful affiliate marketing is the meal delivery service, Purple Carrot. The company started a brand new affiliate program and saw a 68 percent increase in orders and a 30 percent increase in return on ad spend in the first few months*.
Brands only pay when results are achieved, which means the channel carries low risk and high growth potential.
Results from a Performance Marketing Association survey found that return on ad spend (ROAS) for the affiliate channel delivered a 12:1 return (excluding financial institutions).* Our handy affiliate program investment calculator* is a great tool for uncovering what your ROI could be if you invest in Impact’s Partnership Cloud™.
Meanwhile, affiliates can partner with brands that align with their own values. All an affiliate needs to do is to share a link on its website and across its social channels. In return, the affiliate will enjoy uncapped earnings potential for traffic it sends to the brand’s website — whether that’s payment on first click or for any converting sales. Joining a brand’s affiliate program is usually free, so there’s little to no risk for the affiliate.
What are affiliate partnerships?
The affiliate marketing channel has been around since the late 1990s, but it’s gone through some serious changes in recent years. Strategies that worked just a few years ago are no longer ideal. But affiliate partnerships offer a viable new way to think about relationships with affiliate publishers.
Affiliate partnerships today nurture long-term relationships with affiliates, and include full life cycle management — from recruitment to reoptimization — with meaningful insights. The affiliate partnership approach enables advertisers to gain a deeper understanding of performance. Brands also can analyze customer value and view the full consumer journey.
For a complete overview of the history of the affiliate channel and how the strategy has evolved, check out our ebook, Affiliate marketing is dead*
What are the different types of affiliate marketing partners?
Each affiliate partner type reaches its audience in a different way, such as a blog post, coupon website, or email campaign. Each partner type engages with customers at different stages of the consumer journey. For example, a social media influencer could raise awareness at the beginning of the consumer journey, while a coupon publisher may help close a sale at the end of it.
Here are the most common types of affiliate partnerships:
- Content partner: The partner creates content, such as blog posts or product guides, to tell consumers about a brand’s products or services.
- Coupons and deals: The partner promotes a brand by offering discount codes or highlighting promotional deals.
- Affiliate tools: Tools that act as sub-affiliate networks and give sub-affiliate partners ways to easily monetize their content (e.g., VigLink, Skimlinks, etc.).
- Mobile app affiliate: The partner uses their app to drive traffic to a brand’s website/app.
- Email marketer: The partner engages with its email audience to promote a brand.
- Social media influencers and communities: These partners use social media platforms such as Instagram, Facebook, and YouTube to tell their audience about a brand.
- Directories: These partners have data-feed-driven websites and usually surface product or price comparisons.
- Loyalty, rewards, and cashback: These partners give consumers a cut of their affiliate commissions in the form of cashback or loyalty rewards.
- Paid search affiliate: The partner bids on paid search terms to drive traffic to a brand’s website.
- Pay-per-call partners: These partners prompt consumers to call a brand. The brand tracks the calls and accordingly awards the partners credit.
- Toolbars: Toolbar partners have browser extensions that allow consumers to apply promo codes or automatically check for cashback.
- Vloggers: Video bloggers promote a brand in their video blogs. Examples include product unboxings or product video reviews.
- B2B: Brands may partner with other brands to form strategic brand-to-brand partnerships.
2. Understanding how an affiliate marketing program works
Whether you plan to create an affiliate program or join one, it’s a good idea to learn how affiliate programs work. Let’s dive into the basics.
What is an affiliate program?
An affiliate program is the process or system a brand creates to manage affiliate marketing relationships. Brands create and manage programs that affiliates can join. The goal is to support the relationship between a brand and its affiliate partners. This includes onboarding (recruitment), contracts, payments, and sharing opportunities. Each affiliate program has its own set of terms and conditions.
An affiliate program includes three parties:
- The affiliate
- The brand or enterprise
- The affiliate network/software as a service (SaaS) solution
Advertisers can use a SaaS solution to manage their partners or an affiliate network. We’ll cover this more in-depth later.
The best way to describe the way an affiliate program works is to break down the affiliate’s journey and look at the road to payout.
The road to payout
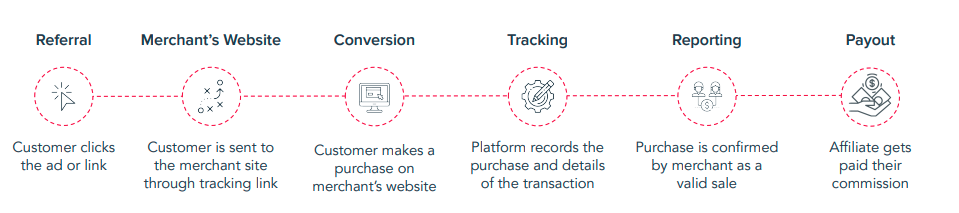
How does affiliate tracking work?
An advertiser gives affiliates access to tracking links that track their clicks. Some affiliate programs allow partners to customize the look of these links. Many brands also create specific landing pages on their websites that affiliates can link to.
To track specific conversion events, brands may use one of the following tracking methods:
- Javascript tags — the most common tracking method. Javascript tags capture a wide variety of data points, which enhances reporting and commissioning capabilities. Javascript tags enable real-time tracking of clicks, conversions, and website behavior.
- Image pixels — a less robust tracking method used to track clicks and conversions. Image pixels still allow for real-time tracking, but with fewer data points.
- API calls — also known as server-to-server tracking, application programming interface (API) calls submit conversion data via a web service API call to a SaaS platform or affiliate network. API calls do not need cookies to operate, and can work in real time or in delayed intervals. This is the most futureproof methodology* available today.
- FTP tracking — another version of server-to-server tracking. This method uses an FTP server to either receive or push tracking data. Advertisers create a “.CSV” file of all the conversions that have occurred on their website, and submit them to Impact via FTP.
These are all good tracking methods to use for now. But keep in mind that Google has expressed its intent to completely remove third-party cookies*. To get ready for this change and futureproof your affiliate program, APIs remain the most reliable tracking method. They don’t rely on third-party cookies and enable brands to circumvent browser policies.
Advertisers can communicate with tech platforms through APIs. APIs do not rely on browsers as intermediaries, which reduces the amount of data shared. API tracking also improves attribution (i.e., the ability to attribute user activity in the full consumer journey).
Ready to start your partnership program?
Talk with our team of partnership experts
3. Affiliate marketing platforms and networks
Every affiliate program needs the right technology behind it. If you want to grow an affiliate program you have two main options:
1. Affiliate networks
Networks give advertisers access to a large pool of affiliates. It’s easy to find relevant affiliates, and onboarding is straightforward. However, you will be limited to the affiliates within the network. Networks frequently bundle services into their offering.
2. Software solutions
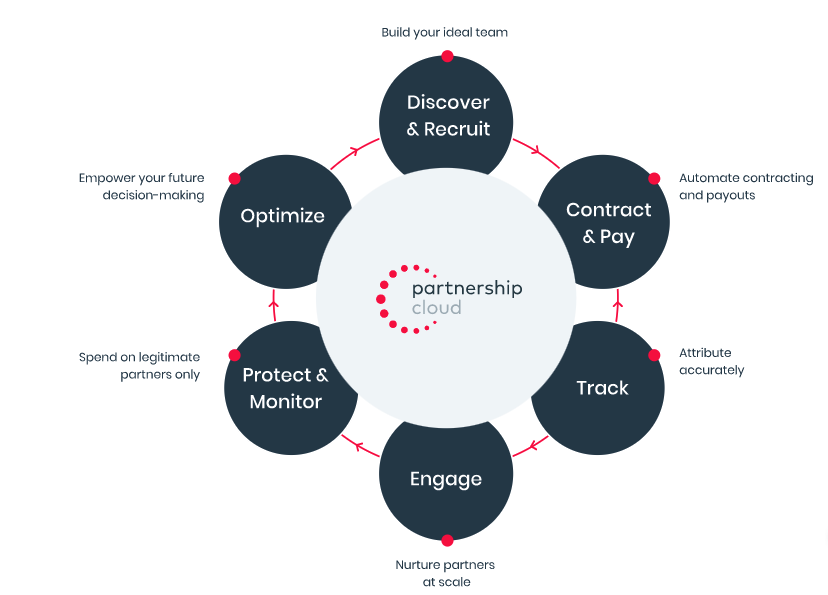
SaaS solutions or partnership platforms offer brands flexibility and control by allowing them to work with anyone they want, not just publishers within a network. SaaS platforms help brands automate their program management across the entire partnership life cycle: discovery, recruitment, contracts, payouts, tracking, engagement, protection, monitoring, and optimization.
How to choose the right affiliate platform for your brand
Every successful affiliate program uses an affiliate platform to help with program management. The most popular affiliate platforms are SaaS solutions or affiliate networks*. The table below provides a breakdown of the differences between these platform types. Whichever solution you choose, it ideally will help you use automation to manage your affiliates throughout their entire life cycle*.
| SaaS solutions | Affiliate network solution | |
| Discovery and recruitment | Find and attract high-value affiliate partners that drive incremental value. SaaS enables diversification and leads to growth. Brands can bring in various affiliates from outside a network — even those outside the scope of their competitors. | Easy plug-and-play access to a large pool of affiliates that drive a surge in traffic. However, advertisers cannot access partners outside the network. |
| Contracts and payouts | Customized payouts and rewards that drive value at any point in the conversion funnel. | Simple payments and contracts that reward affiliates through commissions. Usually based on last-click results. |
| Customer experience / user control | Direct access to partners provides control over the customer experience. Also allows you to collect detailed feedback on engagement. | Your brand is one degree removed from the publishers or affiliates driving traffic. Therefore, consumer behavior may be more challenging to identify. |
| Communication and engagement | Engage affiliate partners at scale with automated messages. Partners can receive custom messages when they hit a milestone or make their first sale. | Work with popular high-profile affiliates, but keep in mind they can be difficult to engage outside a network. And, as they are nonexclusive, these affiliates can work with your competitors. |
| Life cycle management | Streamlined workflows make your job easier. You can recruit, onboard, and manage each partner on the same platform. | An account manager manages your workflows using standard filters. This may include inactive and duplicate affiliate shortlists along the way. |
| Performance and reporting | Instant access to performance metrics and clear, actionable insights. You’ll also have access to multiple touchpoints in the conversion funnel. | Standard reports are available upon request or at agreed-upon monthly or quarterly increments. You’ll likely need support from an account manager to work with and translate data. |
| Security and fraud detection | Your data is your most powerful affiliate fraud detection tool*. Look for a SaaS partnership solution that identifies and blocks fraudulent partners. | Affiliate networks are now more diligent about fraud, but the process is often manual. An “easy win” traffic-led commission structure may also incentivize unethical groups.* (They find loopholes that undermine basic fraud-prevention tools and processes.) |
How to get started with affiliate marketing as an affiliate
It’s not just brands that enjoy the benefits of affiliate marketing technology. There are so many great affiliate programs, networks, and platforms affiliates can join, too. But before you take that step, it’s worth considering your own goals and values as an affiliate.
Things to consider when becoming an affiliate:
- What types of products or services do you want to promote?
- Do you want to promote smaller niche brands — or more popular ones?
- Do you have in mind specific brands for partnerships?
- Do you aspire to any affiliates that you can learn from?
- Do you have the traffic, engagement, or appeal to attract brand partnerships?
- Do you only want to support sustainable or ethical brands?
If you’re yet to acquire a large following or significant website traffic, work on that first. Create regular content and posts to drive engagement, and learn from affiliates that you aspire to as well. You can find many tutorials and resources online, including these tips on how to generate high-quality traffic for your website*. If you have the audience, the engagement, and feel ready to dive in, your next step is research!
3 Things to ask yourself before joining an affiliate network
Before you dive in and sign up with every single network and platform you can find, ask yourself:
1. Which payment model would I find the most beneficial?
Are your fans likely to buy on that first click, or will they return and purchase later? Do you seek a basic commission structure through an affiliate network? Or customized payments that pay for first click or awareness through a platform? (We talked a bit about the different types of affiliate payment models earlier.)
2. Does my audience match the type of products or services I plan to promote?
If your fan base is Gen Z, you’re not going to get much from a partnership with a 50+ brand. Think about the brands that aspire to reach your audience. If you have no idea who your audience is, find out. Use website and social media analytics to run reports. This will help you build your proposition as an affiliate and reach the right brands.
3. Do I want lucrative deals, or simply anything that sticks?
A big affiliate network offers loads of opportunity, but also tons of competition. If you can prove your value as an affiliate, it’s worth joining affiliate programs for brands you love. Affiliate partnership platforms can enable direct contact with brands, and exclusive partnerships as well.
If you’re not sure where to start, check out this ebook: a detailed walk through how to get started as a partner on Impact.
Once you are ready to sign up you can join the Impact partnership network.
What’s next?
You can become the go-to expert on all things affiliate marketing in your organization. Join the Partnerships Experience Academy program for free to elevate your career. Learn more about the certification and courses here.





